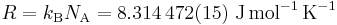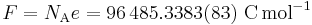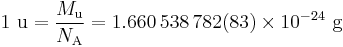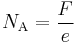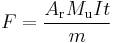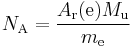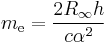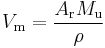Avogadro constant
In chemistry and physics, the Avogadro constant (symbols: L, NA) is defined as the ratio of the number of entities (usually atoms or molecules) N in a sample to the amount of substance n (unit mole) through the relationship NA = N/n.[1] Thus it is the proportionality factor that relates the molar mass of an entity, i.e. the mass of 1 mole of substance, to the mass of said entity.[2] The Avogadro constant expresses the number of elementary entities per mole of substance and it has the value 6.02214179(30)×1023 mol-1.[2][3] [4]
Previous definitions of chemical quantity involved Avogadro's number, a historical term closely related to the Avogadro constant. Revisions in the base set of units of the International System of Units (SI) necessitated redefinitions of the concepts of chemical quantity. Avogadro's number was defined by Perrin as the number of molecules in one gram-molecule of oxygen and it is also the count of elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012kg of the isotope carbon-12[5] Thus, Avogadro's number is a dimensionless quantity and has the numerical value of the Avogadro constant.
| Values of NA[6] | Units |
|---|---|
| 6.02214179(30)×1023 | mol−1 |
| 2.73159757(14)×1026 | lb-mol−1 |
| 1.707248479(85)×1025 | oz-mol−1 |
Contents |
History
The Avogadro constant is named after the early nineteenth century Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro, who, in 1811, first proposed that the volume of a gas (at a given pressure and temperature) is proportional to the number of atoms or molecules regardless of the nature of the gas.[7] The French physicist Jean Perrin in 1909 proposed naming the constant in honor of Avogadro.[8] Perrin won the 1926 Nobel Prize in Physics, in a large part for his work in determining the Avogadro constant by several different methods.[9]
The value of the Avogadro constant was first indicated by Johann Josef Loschmidt who, in 1865, estimated the average diameter of the molecules in air by a method that is equivalent to calculating the number of particles in a given volume of gas.[10] This latter value, the number density of particles in an ideal gas, is now called the Loschmidt constant in his honour, and is approximately proportional to the Avogadro constant. The connection with Loschmidt is the root of the symbol L sometimes used for the Avogadro constant, and German language literature may refer to both constants by the same name, distinguished only by the units of measurement.[11]
Perrin originally proposed the name Avogadro's number (N) to refer to the number of molecules in one gram-molecule of oxygen (exactly 32g of oxygen, according to the definitions of the period),[8] and this term is still widely used, especially in introductory works.[12] The change in name to Avogadro constant (NA) came with the introduction of the mole as a base unit in the International System of Units (SI) in 1971,[13] which recognized amount of substance as an independent dimension of measurement.[14] With this recognition, the Avogadro constant was no longer a pure number, but had a unit of measurement, the reciprocal mole (mol−1).[14]
While it is rare to use units of amount of substance other than the mole, the Avogadro constant can also be defined in units such as the pound mole (lb-mol) and the ounce mole (oz-mol).
- NA = 2.73159757(14)×1026 lb-mol−1 = 1.707248479(85)×1025 oz-mol−1
General role in science
Avogadro's constant is a scaling factor between macroscopic and microscopic (atomic scale) observations of nature. As such, it provides the relation between other physical constants and properties. For example, it establishes a relationship between the gas constant R and the Boltzmann constant kB,
and the Faraday constant F and the elementary charge e,
The Avogadro constant also enters into the definition of the unified atomic mass unit, u,
where Mu is the molar mass constant.
Measurement
Coulometry
The earliest accurate method to measure the value of the Avogadro constant was based on coulometry. The principle is to measure the Faraday constant, F, which is the electric charge carried by one mole of electrons, and to divide by the elementary charge, e, to obtain the Avogadro constant.
The classic experiment is that of Bowers and Davis at NIST,[15] and relies on dissolving silver metal away from the anode of an electrolysis cell, while passing a constant electric current I for a known time t. If m is the mass of silver lost from the anode and Ar the atomic weight of silver, then the Faraday constant is given by:
The NIST scientist devised a method to compensate for silver lost from the anode by mechanical causes, and conducted an isotope analysis of the silver used to determine the average atomic weight. Their value for the conventional Faraday constant is F90 = 96,485.39(13) C/mol, which corresponds to a value for the Avogadro constant of 6.0221449(78)×1023 mol−1: both values have a relative standard uncertainty of 1.3×10−6.
Electron mass measurement
The Committee on Data for Science and Technology (CODATA) publishes values for physical constants for international use. It determines the Avogadro constant[16] from the ratio of the molar mass of the electron Ar(e)Mu to the rest mass of the electron me:
The relative atomic mass of the electron, Ar(e), is a directly-measured quantity, and the molar mass constant, Mu, is a defined constant in the SI. The electron rest mass, however, is calculated from other measured constants:[16]
As may be observed in the table of 2006 CODATA values below,[6] the main limiting factor in the precision of the Avogadro constant is the uncertainty in the value of the Planck constant, as all the other constants which contribute to the calculation are known more precisely.
| Constant | Symbol | 2006 CODATA value | Relative standard uncertainty | Correlation coefficient with NA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electron relative atomic mass | Ar(e) | 5.485 799 0943(23) × 10–4 | 4.2 × 10–10 | 0.0082 |
| Molar mass constant | Mu | 0.001 kg/mol | defined | — |
| Rydberg constant | R∞ | 10 973 731.568 527(73) m−1 | 6.6 × 10–12 | 0.0000 |
| Planck constant | h | 6.626 068 96(33) × 10–34 Js | 5.0 × 10–8 | –0.9996 |
| Speed of light | c | 299 792 458 m/s | defined | — |
| Fine structure constant | α | 7.297 352 5376(50) × 10–3 | 6.8 × 10–10 | 0.0269 |
| Avogadro constant | NA | 6.022 141 79(30) × 1023 mol−1 | 5.0 × 10–8 | 1 |
X-ray crystal density (XRCD) method
A modern method to determine the Avogadro constant is the use of X-ray crystallography. Silicon single crystals may be produced today in commercial facilities with extremely high purity with few lattice defects. This method defines the Avogadro constant as the ratio of the molar volume, Vm, to the atomic volume Vatom.
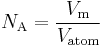 ,
,
where Vatom = Vcell / n. n is the number of atoms per unit cell of volume Vcell.
The unit cell of silicon has a cubic packing arrangement of 8 atoms, and the unit cell volume may be measured by determining a single unit cell parameter, the length of one of the sides of the cube, a.[17]
In practice, measurements are carried out on a distance known as d220(Si), which is the distance between the planes denoted by the Miller indices {220}, and is equal to a/√8. The 2006 CODATA value for d220(Si) is 192.0155762(50) pm, a relative uncertainty of 2.8×10−8, corresponding to a unit cell volume of 1.60193304(13)×10−28 m3.
The isotope proportional composition of the sample used must be measured and taken into account. Silicon occurs in three stable isotopes (28Si, 29Si, 30Si) and the natural variation in their proportions is greater than other uncertainties in the measurements. The atomic weight Ar for the sample crystal can be calculated, as the relative atomic masses of the three nuclides are known with great accuracy. This, together with the measured density ρ of the sample, allows the molar volume Vm to be determined:
where Mu is the molar mass constant. The 2006 CODATA value for the molar volume of silicon is 12.058 8349(11) cm3mol−1, with a relative standard uncertainty of 9.1×10−8.[18]
As of the 2006 CODATA recommended values, the relative uncertainty in determinations of the Avogadro constant by the X-ray crystal density method is 1.2×10−7, about two and a half times higher than that of the electron mass method.
International Avogadro Coordination
The International Avogadro Coordination (IAC), often simply called the "Avogadro project", is a collaboration begun in the early 1990s between various national metrology institutes to measure the Avogadro constant by the X-ray crystal density method to a relative uncertainty of 2 × 10−8 or less.[19] The project is part of the efforts to redefine the kilogram in terms of a universal physical constant, rather than the International Prototype Kilogram, and complements the measurements of the Planck constant using watt balances.[20][21] Under the current definitions of the International System of Units (SI), a measurement of the Avogadro constant is an indirect measurement of the Planck constant:
The measurements use highly polished spheres of silicon with a mass of one kilogram. Spheres are used to simplify the measurement of the size (and hence the density) and to minimize the effect of the oxide coating that inevitably forms on the surface. The first measurements used spheres of silicon with natural isotopic composition, and had a relative uncertainty of 3.1 × 10−7.[22][23][24] These first results were also inconsistent with values of the Planck constant derived from watt balance measurements, although the source of the discrepancy is now believed to be known.[21]
The main residual uncertainty in the early measurements was in the measurement of the isotopic composition of the silicon to calculate the atomic weight so, in 2007, a 4.8-kg single crystal of isotopically-enriched silicon (99.94% 28Si) was grown,[25][26] and two one-kilogram spheres cut from it. Diameter measurements on the spheres are repeatable to within 0.3 nm, and the uncertainty in the mass is 3 µg. Full results from these determinations are expected in late 2010.[27]
See also
- Mole Day
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (1993). Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, 2nd edition, Oxford: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0-632-03583-8. p. 4. Electronic version.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mohr, Peter J.; Taylor, Barry N.; Newell, David B. (2008). "CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2006". Rev. Mod. Phys. 80: 633–730. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.80.633. http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Constants/codata.pdf. Direct link to value.
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Commission on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Abundances, P.; Peiser, H. S. (1992). "Atomic Weight: The Name, Its History, Definition and Units" (PDF). Pure Appl. Chem. 64: 1535–43. doi:10.1351/pac199264101535. http://www.iupac.org/publications/pac/1992/pdf/6410x1535.pdf. Retrieved 2006-12-28.
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Commission on Quantities and Units in Clinical Chemistry, H. P.; International Federation of Clinical Chemistry Committee on Quantities and Units (1996). "Glossary of Terms in Quantities and Units in Clinical Chemistry (IUPAC-IFCC Recommendations 1996)" (PDF). Pure Appl. Chem. 68: 957–1000. doi:10.1351/pac199668040957. http://www.iupac.org/publications/pac/1996/pdf/6804x0957.pdf. Retrieved 2006-12-28.
- ↑ International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (8th ed.), pp. 114–15, ISBN 92-822-2213-6, http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/pdf/si_brochure_8_en.pdf
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Mohr, Peter J.; Taylor, Barry N.; Newell, David B. (2008). "CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2006". Rev. Mod. Phys. 80: 633–730. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.80.633. http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Constants/codata.pdf. Direct link to value.
- ↑ Avogadro, Amadeo (1811). "Essai d'une maniere de determiner les masses relatives des molecules elementaires des corps, et les proportions selon lesquelles elles entrent dans ces combinaisons". Journal de Physique 73: 58–76. English translation.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Perrin, Jean (1909). "Mouvement brownien et réalité moléculaire". Annales de Chimie et de Physique, 8e Série 18: 1–114. Extract in English, translation by Frederick Soddy.
- ↑ Oseen, C.W. (December 10, 1926). Presentation Speech for the 1926 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- ↑ Loschmidt, J. (1865). "Zur Grösse der Luftmoleküle". Sitzungsberichte der kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften Wien 52 (2): 395–413. English translation.
- ↑ Virgo, S.E. (1933). "Loschmidt's Number". Science Progress 27: 634–49. http://gemini.tntech.edu/~tfurtsch/scihist/loschmid.html.
- ↑ See, e.g., Kotz, John C.; Treichel, Paul M.; Townsend, John R. (2008). Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity (7th ed.). Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0495387037. http://cengagesites.com/academic/kotz.cfm?site=2719§ion=home.
- ↑ Resolution 3, 14th General Conference of Weights and Measures (CGPM), 1971.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 de Bièvre, P.; Peiser, H.S. (1992). "'Atomic Weight'—The Name, Its History, Definition, and Units". Pure Appl. Chem. 64 (10): 1535–43. doi:10.1351/pac199264101535. http://www.iupac.org/publications/pac/1992/pdf/6410x1535.pdf.
- ↑ This account is based on the review in Mohr, Peter J.; Taylor, Barry N. (1999). "CODATA recommended values of the fundamental physical constants: 1998". J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 28 (6): 1713–1852. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.72.351.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Mohr, Peter J.; Taylor, Barry N. (2005). "CODATA recommended values of the fundamental physical constants: 2002". Rev. Mod. Phys. 77 (1): 1–107. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.77.1.
- ↑ Mineralogy Database (2000-2005). "Unit Cell Formula". http://webmineral.com/help/CellDimensions.shtml. Retrieved 2007-12-09.
- ↑ Mohr, Peter J.; Taylor, Barry N.; Newell, David B. (2008). "CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2006". Rev. Mod. Phys. 80: 633–730. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.80.633. http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Constants/codata.pdf. Direct link to value.
- ↑ Avogadro Project, National Physical Laboratory, http://www.npl.co.uk/engineering-measurements/mass-force-pressure/mass/research/avogadro-project, retrieved 2010-08-19.
- ↑ Leonard, B. P. (2007), "On the role of the Avogadro constant in redefining SI units for mass and amount of substance", Metrologia 44 (1): 82–86, doi:10.1088/0026-1394/44/1/012.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Jabbour, Zeina J. (2009), "Getting Closer to Redefining The Kilogram", Weighing & Measurement Magazine (October): 24–26, http://www.nist.gov/customcf/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=903635.
- ↑ Becker, Peter (2003), "Tracing the definition of the kilogram to the Avogadro constant using a silicon single crystal", Metrologia 40 (6): 366–75, doi:10.1088/0026-1394/40/6/008.
- ↑ Fujii, K.; Waseda, A.; Kuramoto, N.; Mizushima, S.; Becker, P.; Bettin, H.; Nicolaus, A.; Kuetgens, U. et al. (2005), "Present State of the Avogadro Constant Determination From Silicon Crystals With Natural Isotopic Compositions", IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 54 (2): 854–59, doi:10.1109/TIM.2004.843101.
- ↑ Williams, E. R. (2007), "Toward the SI System Based on Fundamental Constants: Weighing the Electron", IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 56 (2): 646–50, doi:10.1109/TIM.2007.890591.
- ↑ Becker, P.; Schiel, D.; Pohl, H.-J.; Kaliteevski, A. K.; Godisov, O. N.; Churbanov, M. F.; Devyatykh, G. G.; Gusev, A. V. et al. (2006), "Large-scale production of highly enriched 28Si for the precise determination of the Avogadro constant", Meas. Sci. Technol. 17 (7): 1854–60.
- ↑ Devyatykh, G. G.; Bulanov, A. D.; Gusev, A. V.; Kovalev, I. D.; Krylov, V. A.; Potapov, A. M.; Sennikov, P. G.; Adamchik, S. A. et al. (2008), Dokl. Akad. Nauk 421 (1): 61–64; "High-Purity Single-Crystal Monoisotopic Silicon-28 for Precise Determination of Avogadro's Number", Dokl. Chem. 421 (1): 157–60, 2008.
- ↑ Report of the 11th meeting of the Consultative Committee for Mass and Related Quantities (CCM), International Bureau of Weights and Measures, 2008, p. 17, http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/pdf/CCM11.pdf.
External links
- 1996 definition of the Avogadro constant from the IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology ("Gold Book")
- Some Notes on Avogadro's Number, 6.022 × 1023 (historical notes)
- An Exact Value for Avogadro's Number -- American Scientist
- Avogadro and molar Planck constants for the redefinition of the kilogram